In today’s tech-driven world, terms like “Artificial Intelligence” (AI) and “Machine Learning” (ML) are thrown around constantly. They’re often used interchangeably, leading to a lot of confusion. But while they’re deeply intertwined, they’re not the same thing. Think of it this way: AI is the big, ambitious dream, and Machine Learning is one of the most powerful tools we have to make that dream a reality.
Let’s break it down.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
At its core, Artificial Intelligence is about creating machines that can simulate human intelligence. The goal of AI is to enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human cognitive abilities, such as:
- Learning: Acquiring knowledge and skills.
- Reasoning: Using logic to draw conclusions.
- Problem-solving: Finding solutions to complex challenges.
- Perception: Interpreting sensory information (like images and sounds).
- Understanding natural language: Communicating with humans in a human-like way.
Historically, AI has been a vast field encompassing various approaches, from symbolic AI (rule-based systems) to expert systems. However, in recent years, one particular subfield has truly propelled AI into the mainstream: Machine Learning.
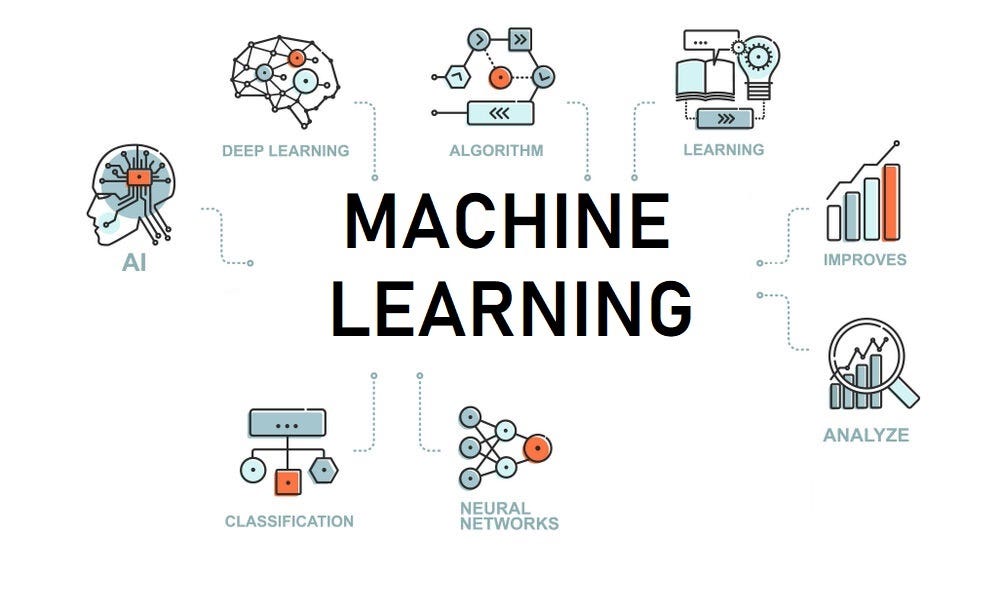
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on enabling systems to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of writing millions of lines of code to cover every possible scenario, ML algorithms are fed vast amounts of data. Through this data, they identify patterns, make predictions, and improve their performance over time.
Imagine teaching a child to identify a cat. You don’t give them a detailed rulebook of “a cat has four legs, fur, whiskers, and meows.” Instead, you show them many pictures of cats and dogs, saying “This is a cat,” or “This is a dog.” Over time, the child learns to distinguish between them. Machine Learning works in a similar fashion.
Key characteristics of Machine Learning:
- Data-driven: ML models rely heavily on large datasets to learn.
- Pattern recognition: They excel at identifying complex patterns and relationships within data.
- Continuous improvement: The more data they are exposed to, the better their performance tends to become.
- Automation of tasks: ML allows for the automation of tasks that are difficult or impossible to program manually.
The Relationship: How ML Fits into AI
So, where does Machine Learning fit into the grand scheme of AI?
ML is a primary driver and a powerful technique for achieving AI. Think of AI as the broad aspiration to create intelligent machines. Machine Learning is the engine that powers many of the most impressive AI applications we see today.
Here’s a simple analogy:
- AI is the entire field of medicine. Its goal is to improve human health.
- Machine Learning is a specialized surgical technique (like minimally invasive surgery) that is incredibly effective for achieving specific medical outcomes.
You can have AI without ML (e.g., old-school rule-based AI systems), but the most advanced and flexible forms of AI today are almost invariably powered by ML.
Why the Confusion?
The interchangeable use of AI and ML often stems from the fact that many cutting-edge AI developments are, in fact, breakthroughs in Machine Learning. When you hear about AI excelling at image recognition, natural language processing, or recommendation systems, you’re almost certainly talking about applications driven by Machine Learning (and often, specifically deep learning, which is a subfield of ML).
Real-World Examples of ML within AI:
- Self-driving cars: ML algorithms process sensor data (cameras, radar, lidar) to understand the environment, predict the behavior of other vehicles, and make driving decisions. This is an AI goal achieved through ML.
- Speech recognition (e.g., Siri, Alexa): ML models are trained on vast amounts of audio data to convert spoken words into text, enabling intelligent assistants to understand and respond.
- Facial recognition: ML algorithms identify and verify individuals by learning patterns from facial features.
- Spam filters: ML models learn from examples of spam and legitimate emails to automatically filter unwanted messages.
- Medical diagnosis: ML algorithms can analyze patient data, scans, and symptoms to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases.
The Takeaway
In essence:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the overarching concept of creating machines that can think, learn, and act like humans.
- Machine Learning (ML) is a powerful and currently the most successful approach to building AI systems, allowing computers to learn from data without explicit programming.
So, the next time you encounter these terms, remember that while they are intimately connected, Machine Learning is a vital tool within the broader, ambitious landscape of Artificial Intelligence. Understanding this relationship is key to demystifying the incredible technological advancements shaping our world.